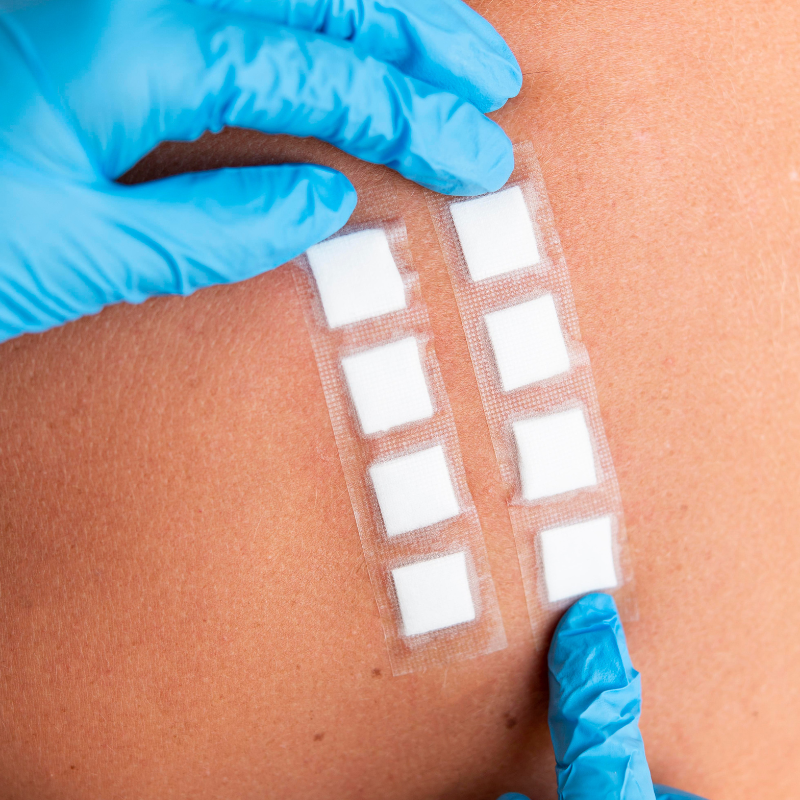
In cosmetic safety assessments, patch testing is a standard method to evaluate skin tolerance and minimize the risk of adverse reactions. But when should it be applied, and what are the best practices to follow? Let’s dive into its role and methodology.
What is Patch Testing in Cosmetics?
Patch testing involves applying a small amount of a cosmetic product on the skin (usually the back or forearm) to monitor potential irritation or sensitization. Patch testing is undertaken for the investigation and confirmation of substances that produce allergic contact dermatitis. It involves applying appropriately diluted allergens to the skin, usually on the back for convenience, for 48 hours. The patch tests are then read at 96 hours as reactions usually take 48–96 hours to develop. Positive reactions produce a patch of dermatitis at the application site of the offending allergen, which will appear as a red and possibly raised, vesicular and even blistering area.
Main goals:
- Assess cosmetic safety before product launch.
- Identify possible allergic or irritant reactions.
- Support regulatory cosmetic dossiers.
When Should Patch Testing Be Used?
Patch testing is recommended in the following cases:
- Before launching a new cosmetic product.
- If the formula contains potential allergens or sensitizers (fragrances, preservatives, dyes).
- After formula modifications of an existing product.
- During consumer studies to confirm skin tolerance in real-life use.
How to Perform Patch Testing in Cosmetic Safety?
Key steps:
- Choose the test site: back or arm, on healthy skin.
- Apply the product under controlled occlusion (patch).
- Exposure time: 24–48 hours.
- Clinical evaluation: a dermatologist or trained assessor interprets skin reactions.
Evaluation criteria:
- No reaction → product considered well tolerated.
- Redness, itching, swelling → possible intolerance or sensitization.
Benefits of Patch Testing in Cosmetics
- Reliable and standardized method for skin safety assessment.
- Protects consumers from unwanted reactions.
- Strengthens regulatory compliance.
- Builds brand credibility with “dermatologically tested” claims.
Conclusion
Patch testing remains a cornerstone of cosmetic safety assessments, ensuring both regulatory compliance and consumer trust. By detecting potential skin reactions early, it helps deliver safer and more reliable products.
👉 Key takeaway: Patch testing is not only a regulatory step but also a quality and safety guarantee in cosmetic development.
Want to dive deeper into cosmetic testing methods and industry news?
➡️ Visit Skinobs to explore more expert insights, articles, and resources.